Introduction:
In the consistently developing scene of memory technology, GDDR6 has arisen as a prominent player, offering high bandwidth and low power consumption. This article delves into the technical intricacies of GDDR6 memory devices, focusing on their security features and the intellectual innovation (IP) trends related to them.
Understanding GDDR6 Memory Devices:
GDDR6 Basics
GDDR6, which represents Graphics Double Data Rate 6, is a type of synchronous graphics random-access memory. It is designed essentially for high-performance graphics cards, gaming consoles, and different applications that request significant memory data transmission bandwidth.
Key Characteristics
High Bandwidth: GDDR6 flaunts impressive data transfer rates, giving significant memory transfer speed to help request workloads in gaming, graphics rendering, and artificial intelligence AI applications.
Low Power Consumption: Notwithstanding its superior execution, GDDR6 is designed with power efficiency, guaranteeing that it can fulfill the needs of modern devices without excessive power consumption.
Architecture and Interface: GDDR6 utilizes a 16n prefetch architecture, meaning it brings 16 data items per clock cycle. It likewise includes a dual-channel design, considering expanded data transfer capacity. The interface operates on a double data rate, meaning information is moved on both the rising and falling edges of the clock signal.
Security Features of GDDR6
ECC (Error-Correcting Code): GDDR6 memory devices frequently integrate ECC functionality. ECC is a system that empowers the detection and correction of errors in stored data. Here information uprightness is of vital significance, like in mission-critical systems or scientific computations.
Thermal Sensors and Protection: Modern GDDR6 modules come furnished with thermal sensors that monitor temperature levels. At the point when temperatures exceed safe thresholds, the memory controller can start thermal throttling or even shut down to prevent damage from overheating.
Secure Boot and Encryption: Some GDDR6 executions support secure boot and encryption features. Secure boot guarantees that only authenticated and trusted firmware can be stacked onto the memory device, mitigating the risk of unauthorized access or malicious code execution.
Physical Security Measures: Physical security features like tamper-evident bundling and coatings, as well as anti-tamper mechanisms, might be executed to safeguard against physical attacks on the memory device.
IP Trends in GDDR6 Memory Devices
High-Density Memory Designs
As interest in higher memory capacity develops, there is a pattern toward creating GDDR6 memory modules with higher capacity densities. This empowers devices to handle larger datasets and more complex applications.
Enhanced Power Efficiency
Persistent efforts are being made to further develop the power efficiency of GDDR6 memory devices. This remembers headways for process innovation, circuit plans, and power management techniques to convey better performance per watt.
Integration with AI and Machine Learning
Given the rising integration of machine learning and AI in different applications, there is a pattern toward improving GDDR6 memory for these responsibilities. This might include explicit memory configurations or enhancements custom-made for artificial intelligence handling.
Advanced Packaging Technologies
Developments in bundling advancements, like 3D stacking and advanced interconnects, are being investigated to improve the exhibition and thickness of GDDR6 memory devices.
GDDR6 IP Developments and Legal Considerations
WCK Clocking
The GDDR6 SGRAM supports two operating modes for WCK frequency which differ in the DQ/DBI_n pin to WCK clock frequency ratio. The GDDR6 SGRAM supports DDR and QDR operating modes for WCK frequency which differ in the DQ/DBI_n to WCK clock frequency ratio.
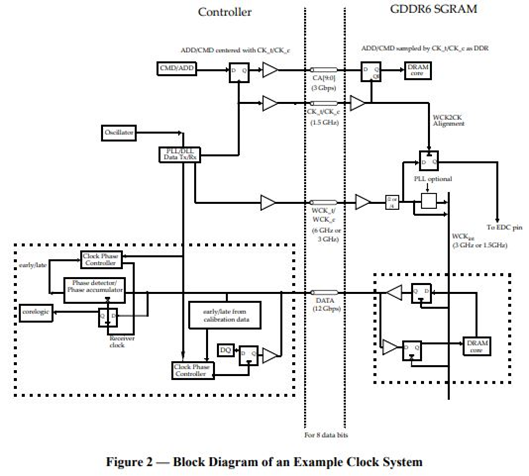
The JEDEC GDDR6 JESD250D standard (source: JEDEC)
IP Landscape
The intellectual property landscape for GDDR6 innovation is dynamic and advancing. Organizations in the semiconductor industry are continuously creating and licensing developments connected with GDDR6 memory configuration, fabricating processes, and related advancements. Licensing agreements and cross-licensing arrangements assume a vital part in permitting organizations to get to and use these IP resources.
Patent Challenges and Litigations
With the rising competitive nature of the innovation business, patent disputes and litigations can emerge. Organizations should be cautious in surveying the potential infringement risks related to GDDR6-related technologies and should participate in due diligence before creating items to stay away from legal complications.
Licensing Strategies
Licensing GDDR6-related IP is a typical methodology for organizations to get to the innovation without wasting time. Licensing arrangements frame the terms under which an organization can utilize licensed innovations, and they might include royalty payments or other monetary considerations. Developing a sound licensing procedure is fundamental to guarantee that organizations can use GDDR6 innovation while regarding IP rights. Intel Corp. holds a maximum number of patents followed by Samsung and Micron.
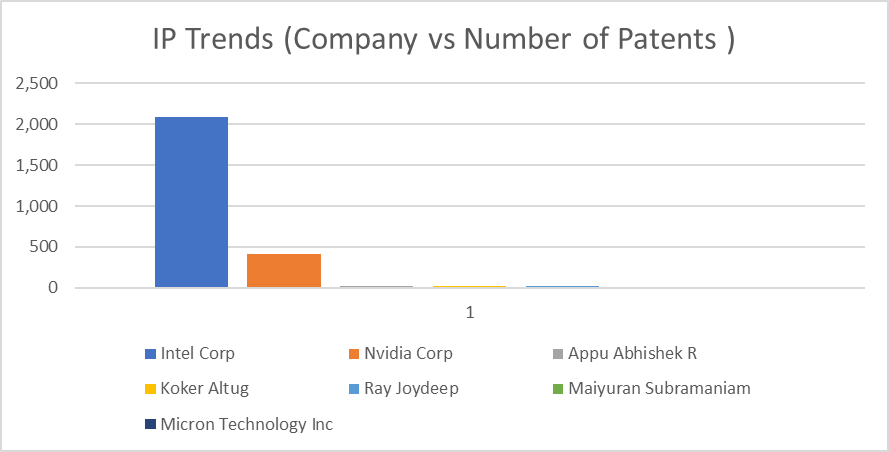
The https://www.lens.org/ (source: https://www.lens.org/lens/search/patent/list?q=GDDR6%20Memory%20Devices%20%20Security%20Features )
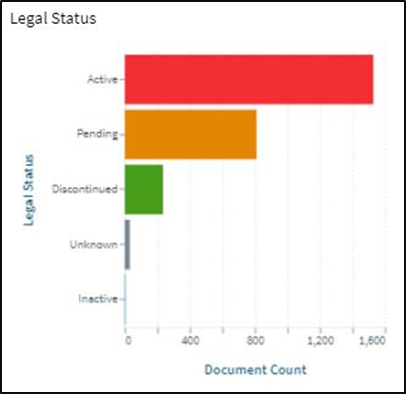
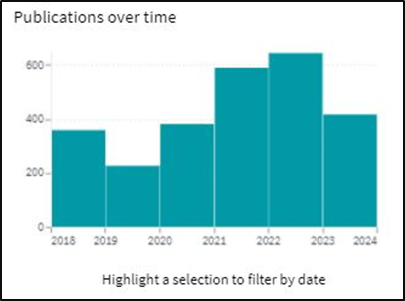
The https://www.lens.org/ (source: https://www.lens.org/lens/search/patent/list?q=GDDR6%20Memory%20Devices%20%20Security%20Features )
Conclusion
GDDR6 memory devices have established themselves as a foundation of superior execution memory innovation. Their blend of high transmission capacity, low power utilization, and security features make them an imperative part of modern computing systems. As innovation keeps on developing, we can anticipate further progressions in limit, power effectiveness, and mix with arising advancements like simulated intelligence and AI. Keeping an eye on these trends will be significant for remaining at the forefront of GDDR6 memory technology.
Meta Data
Delve into GDDR6 memory: Security features & IP trends for high-performance computing.


