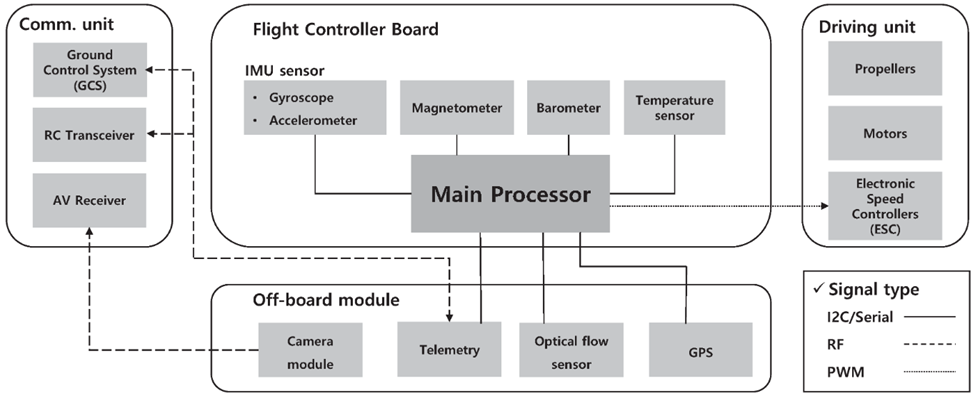
Yangtze Memory Technologies Co., Ltd (YMTC) has remained a leader in its field despite the rapid changes happening around it. Today, we will examine one of their notable products, the X1-9050.
What is the X1-9050?
The X1-9050 is the second generation of YMTC’s 3D NAND flash memory products. An important turning point for the company was reached in August 2019 when it was placed into small-scale mass production. One distinctive feature that makes this product stand out in the market is that it is the first from YMTC to be designed and processed using the Xtacking architecture.
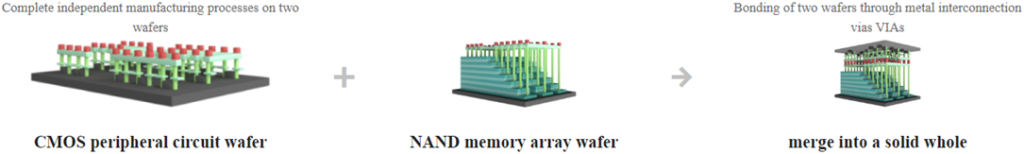
X1-9050 Layout (Source: https://www.ymtc.com/cn/technicalintroduction.html)
With its cutting-edge features and capabilities, the X1-9050 is a storage solution of the future. Its versatility in different settings is attributed to its distinctive characteristics. The X1-9050 can meet your needs whether you’re a professional handling massive volumes of data, a student needing dependable storage for assignments, or a gamer needing fast performance.
X1-9050 Key Features
Advanced Technology
The X1-9050 is a product of advanced technology. It’s built on the Xtacking architecture, which is YMTC’s patented 3D NAND stacking technology. The peripheral and memory cell arrays can now be manufactured independently thanks to this technology, which can greatly increase chip production efficiency.
Increased Speed
The X1-9050 comes with a 256 GB chip capacity, which makes it an excellent choice for those seeking large quantities of storage. It also offers an impressive I/O speed of upto800MT/s.
Future of Storage
The X1-9050 is a revolutionary storage solution that offers advanced technology and impressive features. As data generation continues to rise, it represents the future of digital storage. Supported by mainstream industry controllers, it can be widely used in the development of consumer, enterprise, and mobile storage products, showcasing the future of digital storage.
Other key differentiating features in X1-9050
The X1-9050 stands out for several reasons when selecting a 3D NAND flash memory product. Its blend of high capacity and speed is unquestionably a significant selling point. Yet, past that, the utilization of the Xtacking design offers extra advantages, adding to the item’s general presentation and unwavering quality.
YMTC X1-9050 v/s Acer Predator GM7
The X1-9050 uses the Xtacking architecture. This unique architecture allows for independent manufacturing of the peripheral and memory cell arrays, which can significantly enhance the efficiency of the chip production process. This is a feature that sets the X1-9050 apart from many of its competitors, including the Acer Predator GM7.
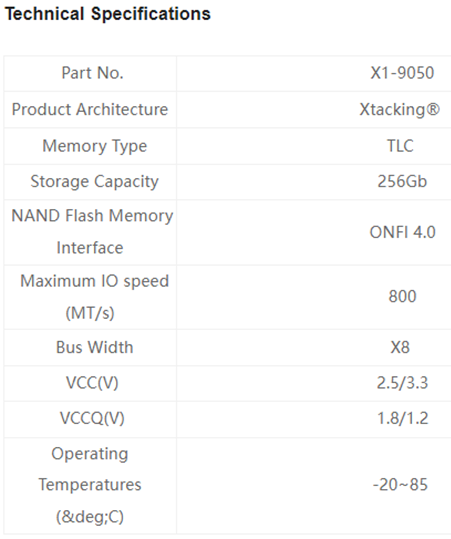
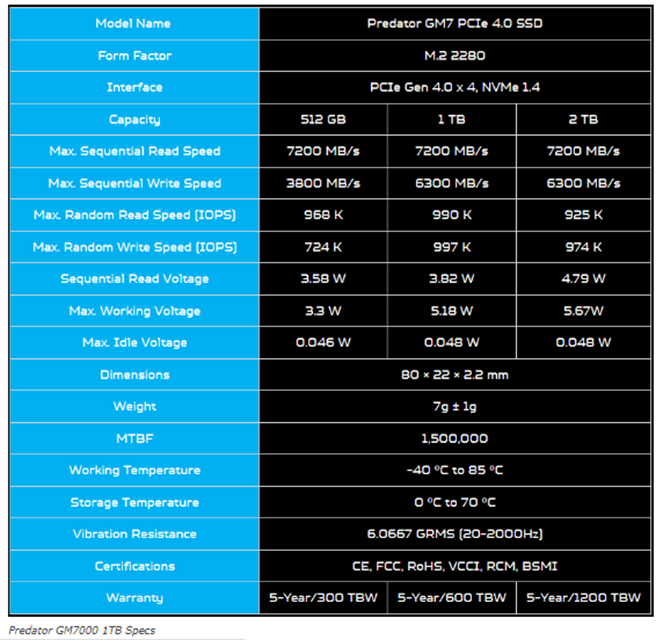
YMTC X1-9050 v/s Acer Predator GM7: Specs comparison (Source: https://www.ymtc.com/en/products/4.html?cat=35 and https://www.servethehome.com/predator-gm7-1tb-pcie-gen4-nvme-ssd-review/)
The X1-9050 likewise offers noteworthy speed. With a chip limit of 256GB, the X1-9050 offers significant extra room. This high capacity makes it a strong decision for those needing huge capacity. While the Acer Hunter GM7 likewise offers significant capacity, the X1-9050’s ability is explicitly intended for 3D NAND flash memory, making it a more particular decision. With a greatest I/O speed that can reach up to 800MT/s, it likewise beats numerous rivals in its class.
Patent Landscape
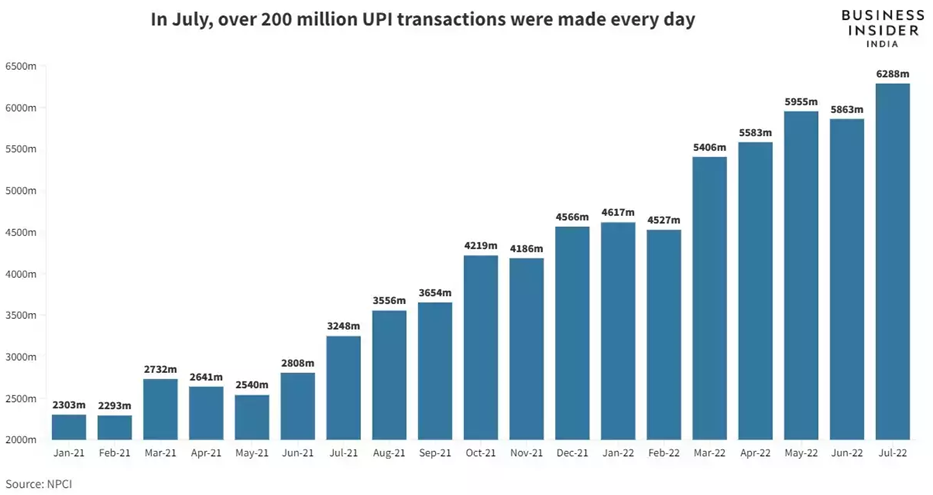
The Yangtze Memory Technologies Co., Ltd. (YMTC) X1-9050, a 2nd-generation 3D NAND flash memory product, has been making waves in the memory industry. The technology landscape surrounding this product is rich and diverse, with a significant increase in patent filings globally. The growth in patent filings for this technology has been remarkable. YMTC has made significant investments in research and development since its inception and has filed more than 4000 memory-related patents. In the years 2020 and beyond, the number of patent application filings increased by 3.97 percent. This development means fast headways in 3D NAND innovation and the rising interest of organizations in this space.
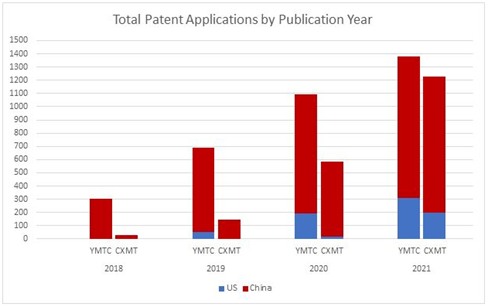
YMTC patent applications per year (Source: https://www.semiconductor-digest.com/china-semiconductor-firms-aggressively-filing-patents-as-they-expand-operations/)
The organization behind the arrival of X1-9050, YMTC is viewed as the pillar behind all the 3D NAND innovations. YMTC has successfully developed 3D NAND SSD products with even higher density by combining their own process and design technology based on Xtacking hybrid bonding. The all-new 232L Xtacking 3.0 TLC is a foundational one and may also guide the development of similar technologies shortly. The Yangtze Memory Technologies Co., Ltd. (YMTC) X1-9050, a 2nd-generation 3D NAND flash memory product, has been making waves in the memory industry.
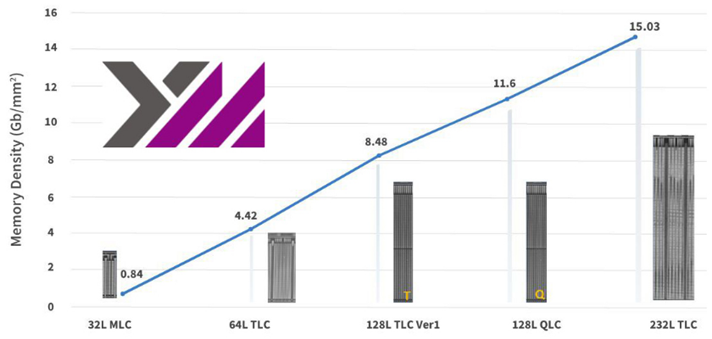
YMTC 3D NAND bit density trend (Source: https://www.techinsights.com/blog/ymtc-leading-pioneer-3d-nand)
Several companies are actively filing patents in this area. YMTC, the creator of the X1-9050, is at the forefront. It has been frequently filing patents and obtaining most of its patent rights in less than 500 days. This could be due to strong innovation or China’s patent policy. In addition to YMTC, other companies like Micron Technology have also been involved in the patent landscape.
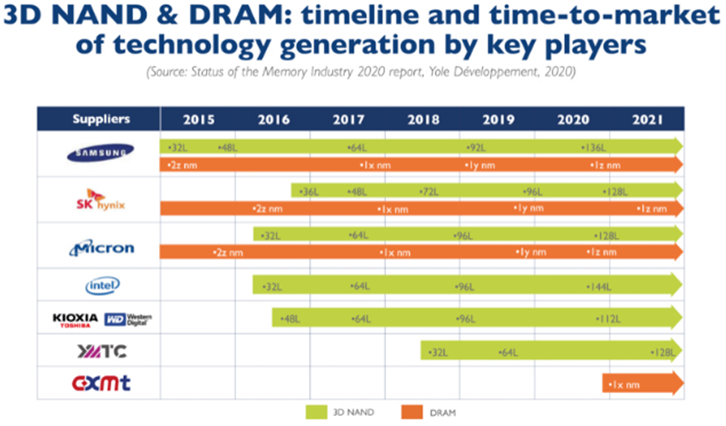
Key manufacturers of 3D NAND (Source: https://www.storagenewsletter.com/2020/11/06/3d-nand-market-to-grow-to-81-billion-in-2025/)
Conclusion
In the rapidly advancing tech industry, the X1-9050 is a testament to YMTC’s commitment to innovation and quality. Whether you’re a consumer looking for reliable storage solutions, or a business seeking to enhance your tech offerings, the X1-9050 is a product worth considering.