SIGNIFICANCE OF WRITEBOOSTER IN UFS
A flash storage specification for digital cameras, cell phones, and other consumer electronics is called Universal Flash Storage (UFS). The 8-lane parallel and half-duplex LVDS interface of eMMCs cannot scale to larger bandwidths as well as the full-duplex serial LVDS interface implemented by UFS. The UFS standard was updated to version 3.1 by JEDEC in January 2020, adding features including Write Booster, Deep Sleep, Performance Throttling Notification, and Host Performance Booster. The significance of WriteBooster mode in UFS and its application to enhancing memory performance will be covered in this essay.
What is WriteBooster mode?
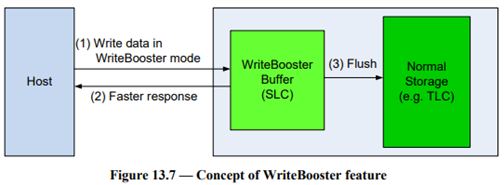
This feature enables UFS storage devices to use a portion of the flash as a pseudo-SLC cache to increase writing performance. This feature enhances the write performance of UFS storage devices, making them faster and more effective, while creating a reserve memory in the flash storage that is easily and frequently accessible. It uses very little space (only 1 bit of data in each cell). Additionally, WriteBooster is a more affordable option that offers comparable performance advantages.
Operation process of WriteBooster mode
The WriteBooster mode in UFS devices operates as follows:
Pseudo SLC Cache
When using WriteBooster mode, flash storage is created with a reserve memory that serves as a pseudo-SLC cache. In the flash storage, this cache is designed to serve as a frequently accessible reserve memory. Just 1 bit of data is stored in each cell, taking up extremely little space while improving write performance.
Write Acceleration
Data is first written to the WriteBooster mode-created pseudo-SLC cache before being written to the UFS storage device. As opposed to writing directly to the flash memory, writing to this cache is quicker. The device can swiftly complete write operations and move on to other activities thanks to the cache’s function as a buffer.
Background Flushing
In the background, the information kept in the pseudo-SLC cache is periodically flushed to the flash memory. By doing this, you may retain the device’s rapid write rates for following operations while also making sure the data is permanently recorded in the flash memory.
Benefits for Performance
WriteBooster mode enhances the write performance of UFS devices by utilizing the pseudo-SLC cache. As a result, write speeds increase, which can speed up application launch, cache loading, browsing performance, and encoding times. Additionally, the feature enhances the responsiveness and general performance of the system.
NOTE: It’s important to keep in mind that the exact UFS device and how it’s implemented may affect whether WriteBooster mode can be enabled or disabled. Disabling WriteBooster mode would result in write operations proceeding as normal writes, without utilizing the pseudo-SLC cache.
Benefits of WriteBooster mode
There are a number of advantages to WriteBooster mode being used with UFS:
Faster Write Speeds
Using a pseudo-SLC cache, WriteBooster mode on UFS devices increases write speeds. Because of the cache, write operations can be completed more quickly, which decreases the amount of time the device needs to be active. The device can reach low-power modes as a result more quickly, increasing power efficiency.
Better Memory Management
By using a piece of the flash as a fictitious SLC cache, WriteBooster mode in UFS improves memory management. Because of the cache, write operations can be completed more quickly, which decreases the amount of time the device needs to be active. The device can reach low-power modes as a result more quickly, increasing power efficiency.
Affordable Alternative
WriteBooster mode in UFS offers comparable performance advantages to pSLC Write Buffer at a lesser price. As a result, it offers a viable option for enhancing memory performance in UFS devices.
Impact of WriteBooster mode on UFS’s power usage
The following ways that WriteBooster mode in UFS affects power usage:
Power Efficiency
By streamlining the writing process, UFS’ Write Booster mode helps to increase power efficiency. The device can write data more quickly and cut down on the time needed for write operations by using a pseudo-SLC cache. As a result, write operations consume less power since the device can perform them more rapidly and effectively.
Deep Sleep Mode
In addition to WriteBooster mode, UFS 3.1 also introduces the Deep Sleep feature. By using voltage regulators for storage and other purposes in addition to power reduction, deep sleep mode reduces energy usage. This improves overall power efficiency by enabling the device to use less power when it is idle or in low-power modes.
Effective Memory Management
Using a piece of the flash as a fictitious SLC cache, WriteBooster mode in UFS improves memory management. Because of the cache, write operations can be completed more quickly, which decreases the amount of time the device needs to be active. The device can reach low-power modes as a result more quickly, increasing power efficiency.
Overall, WriteBooster mode in UFS reduces power usage through write process optimization, the use of a pseudo-SLC cache, and the addition of features like Deep Sleep mode. Through these improvements, devices can write operations more quickly and use less power whether they are idle or in low-power states.
Intellectual property trends for WriteBooster mode in UFS
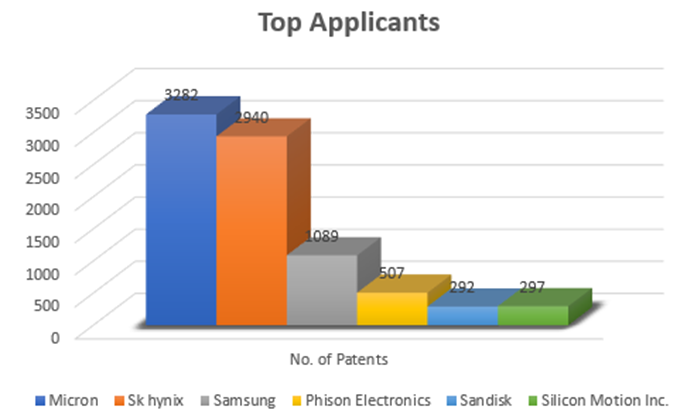
WriteBooster mode in UFS is witnessing rapid growth in patent filing trends across the globe. Over the past few years, the number of patent applications almost doubled every two years.
MICRON is a dominant player in the market with ~3282 patents. So far, it has 2 times more patents than Samsung.
Other key players who have filed for patents in UFS technology with SLC NAND are Sk Hynix, Sandisk, Western Digital etc.
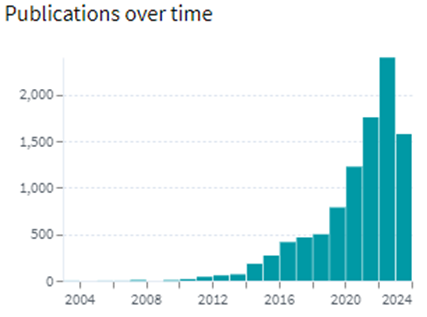
Following are the trends of publication and their legal status over time:
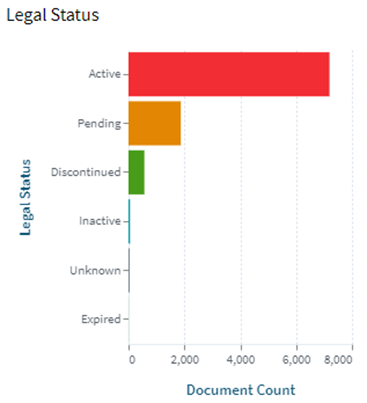
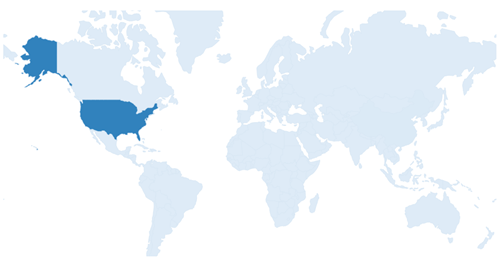
These Top 10 companies own around 60% of total patents related to UFS. The below diagram shows these companies have built strong IPMoats in US jurisdiction.
Conclusion
In conclusion, WriteBooster mode is a crucial component of UFS that boosts write speeds to enhance memory performance. Faster write rates, a pseudo-SLC cache that is easily and repeatedly accessible reserve memory in the flash storage, and a cost-effective solution that offers comparable performance benefits as pSLC Write Buffer are only a few advantages of the implementation of WriteBooster mode in UFS. The significance of UFS’ WriteBooster mode will only increase as mobile devices become more potent and feature-rich. Although Write Booster mode’s effectiveness on UFS devices may vary depending on the specific device, the function is intended to increase write speeds and memory performance, which leads to quicker app startup times, quicker file transfers, and greater system responsiveness.