What is Wi-Fi 7 technology:
In the IT industry, Wi-Fi technology is evolving at a high level. The demand for Wi-Fi technology is increasing day by day everywhere in our daily lives, such as homes, schools, colleges, public Wi-Fi, etc. Even it can be seen in our digital devices such as smartphones, tablets, laptops, computers, etc. Wi-Fi is not only limited to using the internet, it can be used for sharing or transferring data efficiently at higher rates from one device to another devices wirelessly. Wi-Fi allows users to access the internet and transfer data to multiple devices simultaneously using a single Wi-Fi router.
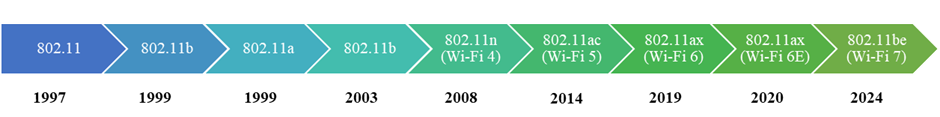
From 1997 to 2023 see Figure 1, Wi-Fi technology is evolving and adding new features in terms of speeds, bandwidth, and channels based on the demands. Researchers are still working on inventions to improve Wi-Fi technology. Starting from 802.11a to 802.11ax, many amendments were made by researchers to improve performance and features. The OFDMA was first introduced in 802.11ax standard also known as Wi-Fi 6 with 6-GHz band in Wi-Fi 6E.
Different Terms or Features of Wi-Fi 7:
Data Rate:
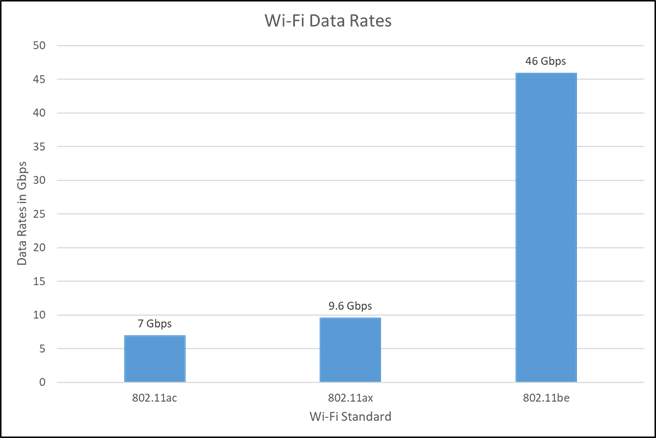
One of the major advantages of the Wi-Fi 7 is the high data rate that claims up to 46Gbps which is 4 times faster than Wi-Fi 6E, Currently the Wi-Fi 6E has a 9.6Gbps very low data rate. In Wi-Fi data rate is the amount of data transmitted through the network in a given amount of time. It refers to the rate at which data is exchanged between devices or between a computer and a peripheral device. More the data rate higher the data transmission speed.
Due to the higher data rate users can access high-speed internet, video streaming in 8K, cloud gaming, and wirelessly transfer large data files from one computer to the computer in a very short time. So, this is the reason why Wi-Fi 7 is needed for the future.
Figure 2 compares the data rate of the prior Wi-Fi versions with Wi-Fi 7.
Channel Bandwidth:
In Wi-Fi 7 the channel bandwidth is also increased to 320MHz. Whereas existing Wi-Fi 6E only supports 160MHz only which is twice than Wi-Fi 7 channel bandwidth. Channel Bandwidth also plays a major role in Wi-Fi technology to deliver massive throughput and high-speed data transmission, the wider the channel more data can be packed and transmitted simultaneously.
In this, the 320MHz channel bandwidth can easily work on the 6GHz band and 160MHz on the 5GHz band. On the other hand, in Wi-Fi 6E 160MHz channel can only work on the 6GHz band due to which it cannot able to transfer data simultaneously at high speed but Wi-Fi 7 can solve this problem.
Figure 3 shows the comparison of channel bandwidth for Wi-Fi 7 and Wi-Fi 6E.

Antenna Technology:
Wi-Fi 7 supports uplink plus downlink 16X16 MU-MIMO (multi-user – multiple input and multiple outputs) to provide double stream and double capacity. It includes multiple antennas as compared to Wi-Fi 6E to provide multiple user uplink and downlink data transmission simultaneously and smoothly, this technology doubles the physical transmission rate with 16 spatial streams.
This feature also allows an access point to communicate simultaneously with multiple user equipment, it reduces the time to wait for the signal for each device which helps to increase the network speed. On the other hand Wi-Fi 6E 8X8 UL or DL MU-MIMO.
4K-QAM:
The Wi-Fi 7 features 4K-QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation). The QAM in wireless technology converts the digital signal into an analog signal. Higher QAM increases the peak rates. The QAM is four times higher than the Wi-Fi 6, that is 1K-QAM, 4K-QAM also adapts the higher-order modulation scheme, it can carry 12 bits per symbol which means in Wi-Fi transmission rate is 20% higher than the Wi-Fi.
This also allows 8K video streaming, live streaming, non-stop cloud gaming, etc.
Multi-RU:
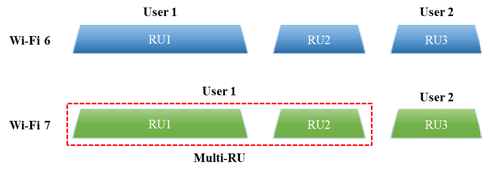
The Wi-Fi 7 assigns multiple RU (resource unit) to a single user to send and receive data frames simultaneously which increases the transmission efficiency. On the other hand, Wi-Fi 6 can only assign a single resource unit to transmit or receive data frames which reduces the efficiency as well as flexibility. Figure 4, shows the Multi-RU comparison with the Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 7.
Preamble Puncturing:
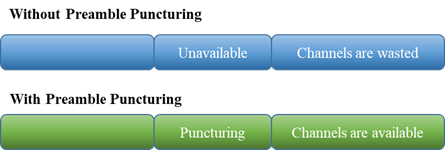
This feature in Wi-Fi 7 allows transmission of the punctured portion of the channel if the channel is busy by other users. For example, if the user equipment communicates over the 320MHz channel but uses only the 20MHz channel, the remaining channel will be reused to other user devices by transmitting the punctured signal. This prevents the wastage of unused channels and opens more channels to be used by other user devices based on the channel requirements. Figure 5 shows the example of the preamble and non-preamble puncturing.
Multi-Link Operation:
The Wi-Fi supports multiple bands that are 2.4GHz, 5GHz, and 6GHz. In Wi-Fi 7 the devices are capable of transmitting and receiving over multiple links simultaneously at different frequency bands. In simple words the devices can use multiple frequency bands simultaneously for data transmission, this increases throughput, latency reduction, improving reliability for 8K video streaming, AR/VR, cloud gaming, etc.
On the other hand, Wi-Fi 6E can support 2.4GHz, 5GHz, and 6GHz frequency bands, however, it cannot simultaneously use frequency bands for data transmission, the devices can use a single frequency band at a time for data transmission (i.e. uses a single link).
Current Wi-Fi 6 technology:
Limitation of Wi-Fi 6E:
The current Wi-Fi 6 technology is still not able to meet the requirements of the users in terms of speed and performance. So, the researchers already started working on the new Wi-Fi technology known as the Wi-Fi 7 which claims that it is 4 times faster than the current Wi-Fi 6 technology, has lower latencies, increased network capacity to support more devices and users, and can provide more performance. The Wi-Fi 7 works on 2.4GHz, 5GHz, and 6GHz bands. Many companies like Qualcomm, Intel, and TP-Link have already started working on the Wi-Fi 7 technology. Moreover, TP-Link and already launched their Mesh Router with Wi-Fi 7 support having Qualcomm Wi-Fi 7 chipset, and IEEE standard 802.11be is also published on the IEEE standard.
WiFi 6E is already in the current market and playing a big role in wireless communication but still, there are many disadvantages such as lower speed, latency issues, network capacity issues, channel utilization issues, bandwidth issues, etc. So, to improve these given problems Wi-Fi 7 was announced which can able to solve the given problems in the future. Technically, there are some main features described as compared to the current Wi-Fi 6 or Wi-Fi 6E technologies. In the real world Wi-Fi 7 claims to provide advantage to users in augmented reality, virtual reality, extended reality, video streaming in 8K, video conferencing and casting simultaneously, cloud high definition gaming, etc.
IEEE 802.11be as WIFI 7:
The Wi-Fi 7 (also known as IEEE 802.11be) is already in the testing phase to provide much more advantages and is expected to be officially released in 2024. Many companies already launched their products such as TP-Link Mesh Router, Qualcomm Wi-Fi 7 chipsets, etc. Companies including Intel are already working on Wi-Fi 7, and Xiaomi is also working on Wi-Fi 7 to bring their Wi-Fi 7-enabled smartphone. Many researchers and inventors are also working on Wi-Fi 7 by adding features and improvements. As we saw based on the demand, new technology is continuously coming in the public.
References:
https://www.qualcomm.com/products/technology/wi-fi/wi-fi-7
https://www.intel.in/content/www/in/en/products/docs/wireless/wi-fi-7.html
https://www.tp-link.com/in/wifi7/
https://www.wired.com/story/what-is-wi-fi-7/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IEEE_802.11be
https://www.commscope.com/insights/the-enterprise-source/wi-fi-7-should-i-stay-or-should-i-go/
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/difference-between-bandwidth-and-data-rate/


