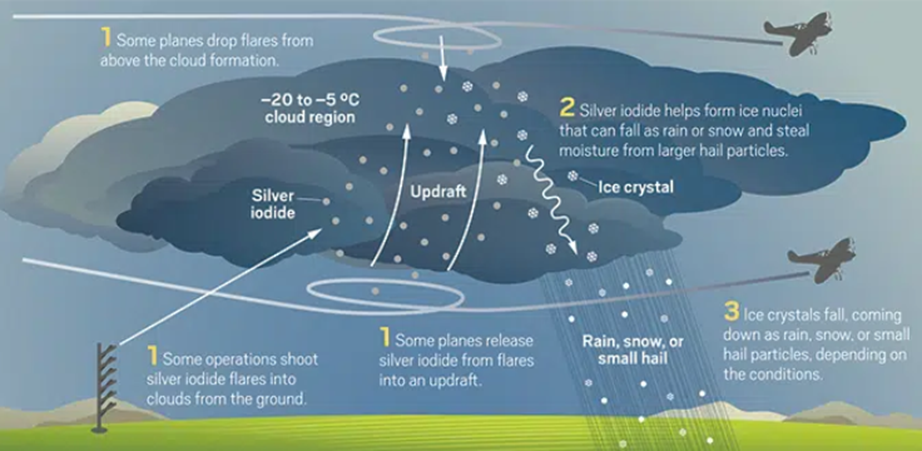
In the latest move of the global streaming wars, Finnish technology leader Nokia (NOKIA TECHNOLOGIES OY) has significantly expanded its U.S. patent enforcement campaign, filing a new lawsuit against Warner Bros. Discovery (WARNER BROS. ENTERTAINMENT INC., WARNER BROS. DISCOVERY, INC., AND HOME BOX OFFICE, INC.) in the Delaware federal court.
This legal action signals Nokia’s uncompromising stance on monetizing its crucial intellectual property related to video compression—the foundational technology that powers high-definition streaming on platforms like Max (formerly HBO Max) and Discovery+.
The Core of the Conflict
The lawsuit, made public this week, directly accuses Warner Bros.’ streaming services of violating Nokia’s patent rights in technology critical for encoding and decoding video.
Nokia’s patented innovations enable the highly efficient compression of raw video files, a process essential for delivering a high-definition experience without crippling bandwidth requirements. In its complaint, Nokia alleges infringement on 13 of its patents, which cover fundamental elements of modern video coding standards.
Nokia’s statement emphasizes its preference for negotiation: “Litigation is never our first choice… we hope Warner will engage with us to reach an agreement to pay for the use of our technologies in their streaming services.”
The complaint confirms that Nokia attempted to negotiate a license with Warner Bros. since 2023, but the companies failed to reach an agreement on fair licensing terms, leaving Nokia to seek an unspecified amount of monetary damages through the court.
A Pattern of Enforcement
The legal action against Warner Bros. Discovery is far from an isolated event; it is part of Nokia’s focused global strategy to secure compensation for its extensive patent portfolio:
- Settled with Amazon Following a multi-jurisdictional legal battle, Nokia successfully resolved its patent disputes with Amazon earlier this year. The settlement covered the use of Nokia’s video technologies in Amazon’s streaming services and devices, validating the strength of Nokia’s claims.
- Ongoing Cases Nokia maintains similar patent infringement cases against other major media companies like Paramount, as well as hardware manufacturers such as Acer and Hisense.
- Global Reach Nokia’s aggressive enforcement includes filing parallel lawsuits against Warner Bros. in major jurisdictions like the Unified Patent Court (UPC), Germany, and Brazil, increasing the legal and commercial pressure on the media giant.
This campaign highlights Nokia’s shift from a device manufacturer to a technology licensor, ensuring its massive investment in research and development—particularly in Standard Essential Patents (SEPs) for video codecs like H.264 and H.265 (HEVC)—is properly rewarded.
Case Details at a Glance
This case will be a key indicator of how courts value the underlying technology that fuels the entire streaming industry, particularly given Nokia’s recent successful resolution with Amazon.
| Legal Detail | Information |
| Case Name | Nokia Technologies Oy v. Warner Bros Entertainment Inc |
| Venue | U.S. District Court for the District of Delaware |
| Case Number | No. 1:25-cv-01337 |
| Nokia Counsel | McKool Smith (Warren Lipschitz, Erik Fountain, etc.) |
| Warner Counsel | Attorney information not yet available |
As streaming platforms continue to compete fiercely for content, this lawsuit serves as a powerful reminder that foundational technological innovation—the very code that keeps the video playing smoothly—remains a highly valuable and contested asset.