Introduction:
LiDAR, an acronym for “light detection and ranging” or “laser imaging, detection, and ranging” is a sensor used for determining ranges by targeting an object or a surface with a laser and measuring the time for the reflected light to return to the receiver. With the functionality of scanning its environment, it is also sometimes called 3D laser scanning. Particularly, LiDAR image registration (LIR) is a critical task that focuses on techniques of aligning or registering lidar point cloud data with corresponding images. It involves two types of data that have different properties and may be acquired from different sensors at different times or under different conditions. With an accurate alignment of LiDAR point clouds and captured 2D images, the registration method results in the most informative understanding of the environment with fine details.
How does LiDAR work?
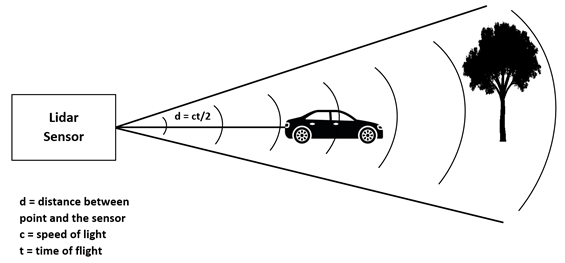
The working methodology of LiDAR includes sending a pulse of light and waiting for the return. It measures the total time period i.e. how long it takes to return the pulse. This finally assists in figuring out the distance between objects.
Fig. 1. Working of LiDAR
Application Areas of LiDAR
The fusion of LiDAR point clouds and camera images is a popular example of Multi-Remote Sensing Image Registration (MRSIR). As of today, LiDAR is of various types and forms such as static and mobile LiDARs. According to the geographical use, LiDAR is of terrestrial, aerial, and marine kinds.
The application of LiDAR is very broad. It has uses in surveying, archaeology, geology, forestry, and other fields such as:
- Autonomous driving: LIR is used to align sensor data to create a more accurate and complete representation of the environment.
- Robotics: Align sensor data to create more accurate maps and enable more precise localization.
- 3D mapping: Align data from multiple sensors to create detailed 3D models of the environment.
- Augmented Reality (AR): Synchronizing virtual elements to correspond with the physical environment.
Utilization of LiDAR in Self-Driving Vehicles
3D Point Cloud and Calculation of Distance
In the realm of road safety, numerous automobile manufacturers are either using or exploring the installation of LiDAR technology in their vehicles.
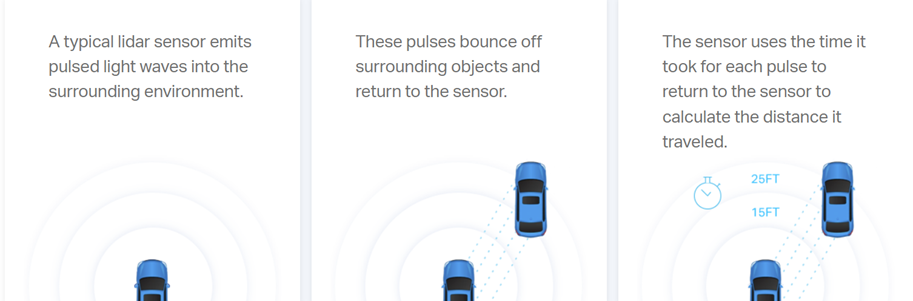
Fig. 1. LiDAR Technology in Self-Driving Vehicles [Source: https://velodynelidar.com/what-is-lidar/#:~:text=A%20typical%20lidar%20sensor%20emits,calculate%20the%20distance%20it%20traveled]
By iterating this process multiple times within seconds, a detailed, live 3D representation of the environment is generated, referred to as a point cloud.
Advantages of Mounting Lidar Above Autonomous Vehicles
Within an autonomous vehicle, the LiDAR sensor captures extensive data through rapid analysis of numerous laser pulses. This information, forming a ‘3D point cloud‘ from laser reflections, undergoes processing by an integrated computer to generate a dynamic three-dimensional representation of the surroundings. Training the onboard AI model with meticulously annotated point cloud datasets becomes pivotal to ensuring the precise creation of this 3D environment by LiDAR. The annotated data empowers autonomous vehicles to detect, identify, and categorize objects, enhancing their ability to accurately discern traffic lanes, road signs, and moving entities, and evaluate real-time traffic scenarios through image and video annotations.
Beyond research, active exploration delves into the use of LiDAR technology within autonomous vehicles. Automakers have begun integrating LiDAR into advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), enabling a comprehensive grasp of dynamic traffic conditions. The journey toward autonomous driving safety relies on these systems, which swiftly make precise decisions through meticulous analysis of vast data points, ensuring security through rapid computations.
Cutting-edge approaches
However, there still are challenges in developing a fully automated vehicle with a guarantee of 100% accuracy in critical tasks such as object detection and navigation. To overcome this challenge, many researchers and automobile companies have been trying to improve this technology. The cutting-edge approaches include broadly categorized architecture of methodologies involving four distinct pipelines: information-based pipeline, feature-based pipeline, ego-motion-based pipeline, and deep learning-based pipeline. There has been more accuracy and improvement in the sector of deep learning-based pipelines. LiDAR technology not only enhances convenience but also plays a pivotal role in reducing severe collisions. The latest advancements in this domain include the innovation of LiDAR sensors and the shift from traditional mechanical methods to cutting-edge FMCW and flash technologies.
Patenting Trends for LiDAR Technology in Autonomous Vehicles
The field of autonomous vehicle technology has witnessed a notable rise in patent submissions, especially concerning sensor technology, mapping techniques, decision-making algorithms, and communication systems. Pioneering the advancements are entities such as Google, Tesla, and Uber, whereas longstanding automotive giants like Ford, General Motors, and BMW have also been actively filing patents. In the United States, a significant emphasis lies on artificial intelligence (AI) and augmented reality within the market, with car manufacturers and developers collaborating to introduce self-driving vehicles to the public. Autonomous cars are predicted to change the driving experience and introduce a whole new set of problems.
Despite Sartre’s initial patent submission in the autonomous vehicle domain, it was perceived primarily as a patent related to an AI system designed for highway navigation or restricted roadways. There was a scarcity of US patent filings for self-driving cars before 2006, largely influenced by a trend that emerged in the late 1990s and persists today: a limited number of patents granted by the US Patent Office.
Challenges in Patenting Technology for Autonomous Vehicles
The challenges in patenting technology for self-driving vehicles emerge when these vehicles are involved in incidents or insurance-related events. Owners typically confront three choices:
- Assuming liability for any harm or property damage caused by their vehicle.
- Taking steps toward legal recourse against the involved driver.
- Exploring compensation from their insurance company to address losses resulting from the other driver’s negligence.
However, legislative uncertainty still clouds the landscape concerning autonomous vehicles and traffic incidents.
Analysis of Patent Applications filed under Lidar in Autonomous Vehicles
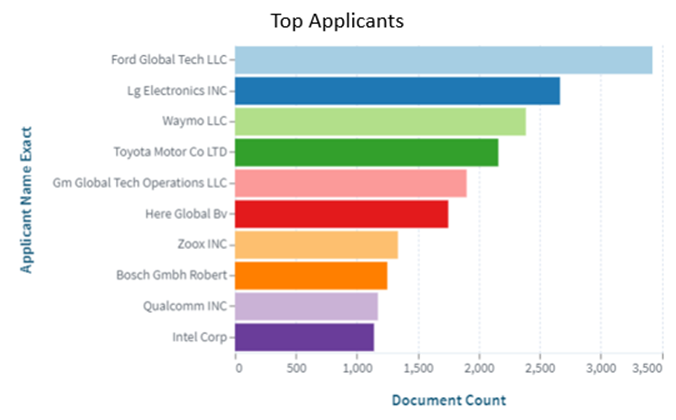
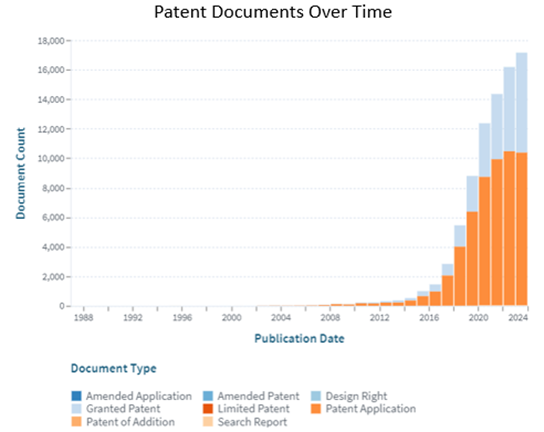
Over the past few years, there has been a rapid growth in filing Patent Applications regarding the use of LiDAR in Autonomous Vehicles. As of today, it is marked that there are ~81,697 patents recorded around the globe. It has been observed that Ford Global Tech LLC with ~3,426 patents is a dominant player in the market. Similarly, LG Electronics and Waymo LLC stand in second and third position in the chart.
[Source: https://www.lens.org/lens/search/patent/list?q=LiDAR%20%20%2B%20Autonomous%20vehicle]
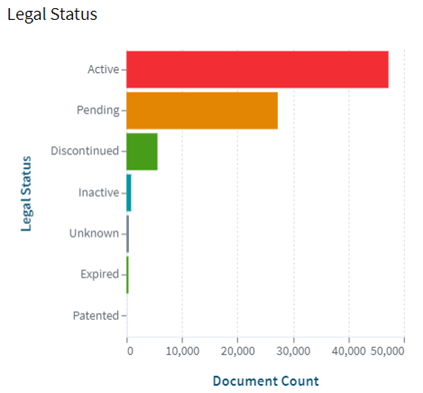
The following visual representations show the charts representing Legal Status and Patent Documents Over Time.
[Source: https://www.lens.org/lens/search/patent/list?q=LiDAR%20%20%2B%20Autonomous%20vehicle]
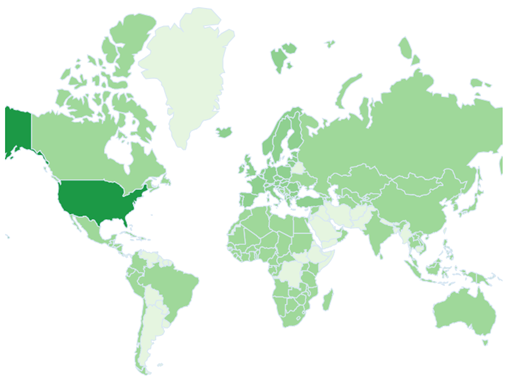
Through an examination of patent filings across different geographic regions, it is evident that the United States, constituting approximately 78% of the overall patents submitted, holds the foremost position in this chart.
[Source: https://www.lens.org/lens/search/patent/list?q=LiDAR%20%20%2B%20Autonomous%20vehicle]
Conclusion
In conclusion, LiDAR technology used in self-driving vehicles has a huge scope in improving road safety. With the cutting-edge FMCW and flash technologies, the application of LiDAR in autonomous vehicles shows great improvements in terms of accuracy and comfort providing features like object detection and incredible navigation. Automobile companies such as Tesla and Toyota have already practiced the technology in their vehicles and companies having such huge turnovers are seeking forward to utilize the full potential of the technology. Technology holds the future of global advancement in technology.