LiFi (light fidelity)
LiFi, short for Light Fidelity, is a wireless communication technology that utilizes visible light to transmit data. It is based on the principle of using light-emitting diodes (LEDs) to send data through rapid variations in light intensity that are invisible to the human eye. Developed as a potential alternative or complement to traditional wireless communication technologies like WiFi, LiFi offers several advantages, including higher data transfer rates, increased security, and reduced electromagnetic interference.
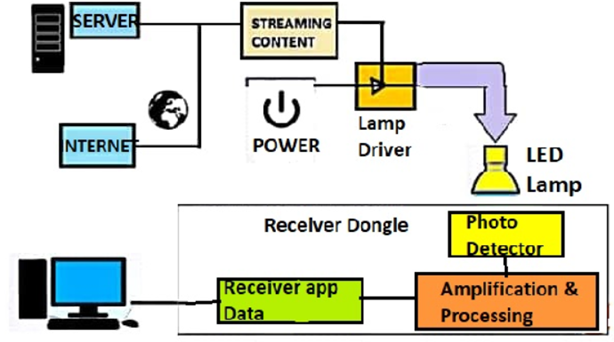
LiFi Architecture (source: semanticscholar)
LiFi (Light Fidelity) architecture is designed to enable wireless communication using visible light as the medium for data transmission. The architecture involves several components and processes to ensure efficient and reliable communication.
Applications of LiFi (light fidelity)
LiFi (Light Fidelity) has a range of applications across different sectors due to its unique advantages, including high data transfer rates, increased security, and reduced electromagnetic interference. Here’s a brief overview of some key applications of LiFi:
- Internet Access:
LiFi can be used to provide high-speed internet access in homes, offices, and public spaces. LED bulbs equipped with LiFi technology can serve as data access points, delivering internet connectivity through visible light.
- Indoor Navigation:
LiFi’s data transmission precision allows for indoor navigation and positioning applications. It can be employed in environments like museums, shopping malls, and airports to provide accurate location-based services.
- Healthcare:
In healthcare settings, LiFi can contribute to secure and high-speed data transmission between medical devices. This is particularly important for applications where the reliability and speed of data exchange are critical, such as in operating rooms or patient monitoring systems.
- Aviation and Automotive:
LiFi technology can enhance in-flight entertainment and communication systems in aviation. In automotive settings, LiFi can contribute to vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communication and entertainment within the vehicle.
- Smart Cities:
LiFi supports the development of smart cities by providing high-speed and reliable connectivity in urban environments. It can be integrated into streetlights, traffic signals, and other infrastructure to create a connected cityscape.
- Underwater Communication:
LiFi’s application is not limited to above-ground environments. It can be employed for underwater communication, where traditional wireless technologies face challenges due to the absorption of radio frequencies in water.
- Secure Environments:
LiFi’s inherent security benefits make it suitable for environments where data security is crucial. Since visible light does not penetrate walls, LiFi signals are confined to specific areas, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Education and Offices:
LiFi can enhance connectivity in educational institutions and office spaces. It offers a high-speed and secure network for students, teachers, and employees, supporting various applications from online learning to collaborative work.
- Retail Environments:
LiFi can be applied in retail for location-based services, personalized shopping experiences, and inventory management. It enables retailers to engage with customers through interactive displays and smart lighting.
- Traffic Management:
LiFi can contribute to intelligent traffic management systems by communicating between vehicles and traffic infrastructure. This can enhance road safety, traffic flow, and overall transportation efficiency. These applications demonstrate the versatility of LiFi technology and its potential to revolutionize the way we access information, communicate, and navigate our surroundings.
Future Perspectives of LiFi (Light Fidelity)
The future perspectives of LiFi (Light Fidelity) hold promising possibilities across various industries, driven by ongoing research, technological advancements, and the unique advantages offered by this wireless communication technology. Here are several key aspects that highlight the future potential of LiFi:
- Integration with 5G:
Complementary Technology: LiFi can complement 5G networks, especially in areas with high data density. The combination of LiFi and 5G could offer a seamless and robust communication infrastructure, providing users with enhanced connectivity and higher data rates.
- Vehicular Communication:
LiFi in the Automotive Industry: LiFi’s potential in the automotive industry could involve in-car communication, entertainment systems, and vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communication. LiFi may contribute to creating a more connected and efficient driving experience.
- Integration with Smart Lighting:
Dual Functionality: As LiFi can be implemented through LED bulbs, it can be seamlessly integrated with smart lighting systems. This dual functionality enhances the efficiency of lighting infrastructure by providing both illumination and data communication.
- Research and Development:
Ongoing Advancements: Continuous research and development in LiFi technology are likely to lead to improvements in data transfer rates, range, and overall performance. Innovations in modulation techniques and system architectures may further broaden the applications of LiFi.
- Global Expansion and Standardization:
Widespread Adoption: LiFi technology may see increased adoption globally as standardization efforts progress. Establishing industry standards can promote interoperability and encourage the development of a diverse ecosystem of LiFi-enabled devices.
- Energy Efficiency:
Green Technology: LiFi’s reliance on LED bulbs, which are energy-efficient, aligns with the growing emphasis on green and sustainable technologies. The energy efficiency of LiFi could contribute to reducing the overall environmental impact of communication technologies.
- Challenges and Solutions:
Overcoming Limitations: Future perspectives of LiFi also involve addressing current challenges, such as signal range limitations and potential interference. Research and development efforts will likely focus on overcoming these limitations to make LiFi more versatile and practical.
Patent Landscape
The intellectual property landscape for LiFi technology is dynamic and advancing. Organizations in the wireless communication industry are continuously creating and licensing developments connected with LiFi and related advancements. Licensing agreements and cross-licensing arrangements assume a vital part in permitting organizations to get to and use these IP resources.
Patent Filling Trends:
LiFi gained significant attention and research interest during this time. Researchers and companies started exploring the potential of LiFi for high-speed, wireless communication using visible light. The initial patent filings during this period likely focused on fundamental aspects of LiFi technology, such as modulation techniques, transceiver designs, and basic communication protocols. Ericsson holds a maximum number of patents followed by Samsung and Signify.
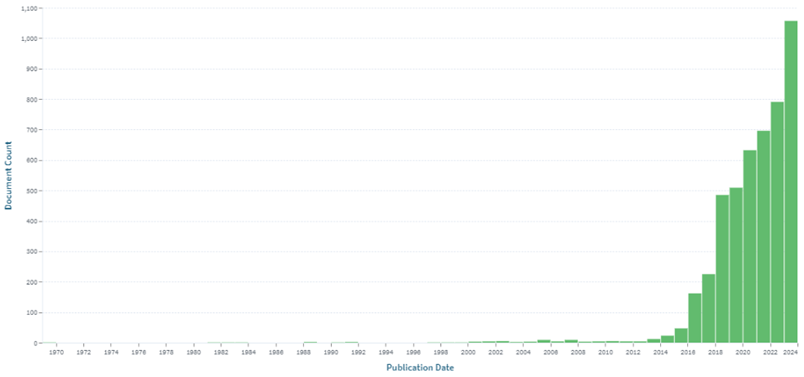
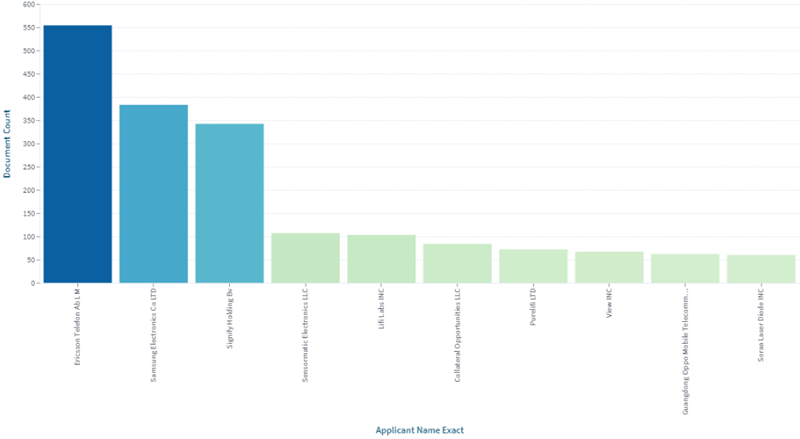
Patent filings ( Source: Lens.org)
The United States has a strong tradition of investing heavily in research and development across various industries. Companies research institutions, and government agencies in the U.S. may contribute significantly to LiFi research, leading to a higher number of patent filings followed by China and Europe.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while LiFi is still in the early stages of commercial deployment, its unique attributes position it as a compelling technology for the future of wireless communication. Ongoing research, standardization initiatives, and advancements in hardware and software are expected to further enhance LiFi’s capabilities and broaden its range of applications in the coming years.

