In an increasingly connected world, where our dependency on mobile devices and data use is rising, the demand for fast and dependable internet access is at an all-time high. But the study found that mobile networks frequently fail to keep up with increased demand, resulting in slower speeds, crowded networks, and disgruntled consumers.
To overcome this issue, WIFI offloading has emerged as a possible alternative. In this blog, we will look at the notion of WIFI offloading, its benefits, and how it works.
WIFI Offloading Understanding:
Wi-Fi offloading is the practice of using Wi-Fi hotspots to keep mobile devices connected. This can be done manually or by logging into a home or public Wi-Fi network. When a device moves from a cellular connection to Wi-Fi or small cell connectivity, such as when mobile traffic is offloaded to public hotspots.
WiFi offloading, or mobile data offloading, diverts cellular network traffic to WiFi networks, improving connectivity and reducing strain on mobile networks. This blog explores the benefits and mechanics of WiFi offloading.
Benefits of WiFi Offloading:
WiFi offloading offers several advantages.
- It enhances connectivity by leveraging faster and more reliable WiFi networks, especially in areas with weak cellular signals.
- It leads to cost savings by reducing mobile data consumption, as WiFi usage doesn’t count towards cellular data caps.
- It reduces network congestion, improving overall network performance during peak usage. Finally, WiFi offloading can extend battery life on mobile devices, as transmitting data over WiFi is more energy-efficient.
How WiFi Offloading Works:
Mobile devices use network selection algorithms to determine the best connection when both cellular and WiFi options are available. Seamless handover ensures uninterrupted connectivity, as devices automatically switch from cellular to WiFi when a connection is available. Authentication protocols and security measures protect data while connected to WiFi networks.
If we speak in technical terms, WiFi offloading refers to a type of handover between a non-WiFi network and a WiFi network.
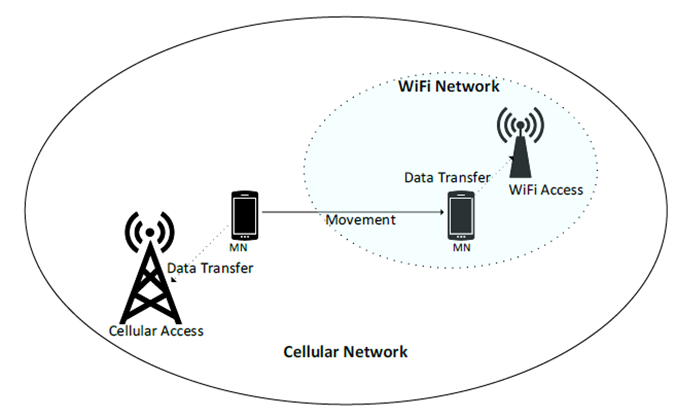
Figure: 1. Mobile data offloading
Source: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Description-of-Mobile-Data-Offloading_fig2_326030064
Let us look into Figure 1. This explains the offloading procedure, so assume that at time t, a mobile node (MN) seeks to initiate a data transfer session. While the cellular network is always presumed to be available, the WiFi network is only accessible when the MN is close enough to the WiFi coverage. The offloading technique employs a network selection algorithm based on Received Signal Strength (RSS).
Received Signal Strength: The Received Signal Strength (RSS) informs the receiver about the strength of the received signal, which represents the power of the signal at the receiving end.
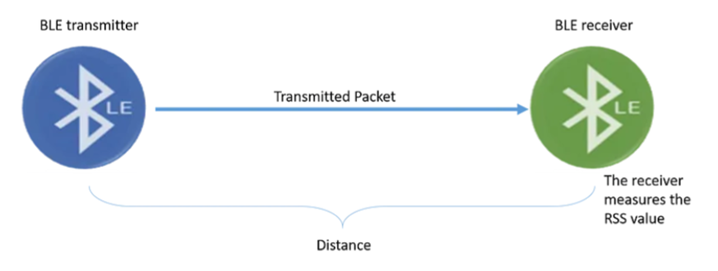
Source: https://pcng.medium.com/received-signal-strength-rss-8a306b12d520
Smartphone operating systems like Android, offer convenient access to the Received Signal Strength (RSS) value when the smartphone receives a Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) packet. By utilizing the Android. Bluetooth SDK, we can retrieve this value through the RSSI variable.
The RSS values can provide valuable insights about the BLE transmitter. One practical application is estimating the distance between our smartphone and the BLE transmitter. We can collect the RSS values at various distances and employ curve-fitting methods to create a ranging model. Alternatively, a simple machine learning approach, such as linear regression, can be applied to learn the ranging model.
Conclusion:
WiFi offloading optimizes connectivity by diverting data traffic to WiFi networks. It offers benefits such as enhanced connectivity, cost savings, reduced network congestion, and improved battery life. As data demands increase, WiFi offloading proves valuable in providing seamless connectivity and addressing network limitations. WiFi offloading works by using network selection algorithms to determine the best connection and ensure seamless handover between cellular and WiFi networks. The Received Signal Strength (RSS) plays a crucial role in this process, providing information about the strength of the received signal.

