Handheld controllers have long defined virtual reality. However, the industry is set to enter a new era in 2025, where the most natural interface will be your hands. For navigating digital environments, controller-less hand tracking is rapidly becoming the norm rather than the exception. The question now is not if it will replace controllers, but how quickly the shift will happen.
How Hand Tracking Works
To map a user’s hand position and movement in three dimensions, controller-less hand tracking combines computer vision, depth sensing, and machine learning. High-speed images of the user’s hands are captured from various angles by arrays of cameras and infrared sensors found in contemporary VR headsets like the Apple Vision Pro and Meta Quest.
Neural networks trained to identify hand shapes, joint locations, and subtle finger movements process these visual inputs. The system then generates a real-time skeletal model of the hand, allowing it to track both small gestures like pinching or tapping and larger motions like grabbing or waving.
Advanced methods such as predictive modelling help reduce latency, ensuring that the virtual hand responds smoothly even if tracking data temporarily drops. Companies like Meta are also integrating wrist-worn electromyography (EMG) sensors, which detect electrical signals from muscle contractions before movement is visible, opening the door to near-instant “thought-driven” control.
Together, these advancements are enabling an accurate, realistic, and immersive interface that mirrors the dexterity of physical touch.
Why It Matters
The significance of hand tracking goes beyond convenience. It improves VR accessibility, especially for beginners who may find conventional controllers intimidating.
Platforms such as Class VR are exploring gesture-based learning, allowing students to manipulate historical artifacts or molecular models naturally. Surgeons are already training using VR simulations, lowering the learning curve by allowing precise practice using natural hand movements.
Games on the Meta Quest show how actions like casting spells, drawing a bow, or throwing objects feel more intuitive with hand gestures. Retail and e-commerce are experimenting with virtual try-on and product visualization, while fitness and rehabilitation apps are integrating hand tracking for more engaging workouts and recovery routines.
By turning the human body into the controller, VR is expanding its applications from classrooms to clinics to living rooms.
Patent Landscape and Graphical Exploration
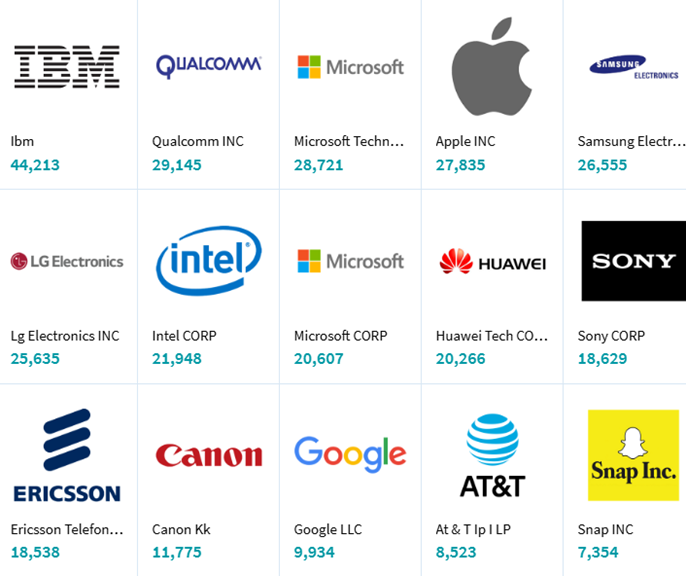
Controller-less Hand Tracking in VR Top Applicants (Source: https://www.lens.org/)
Patent Documents Over Time
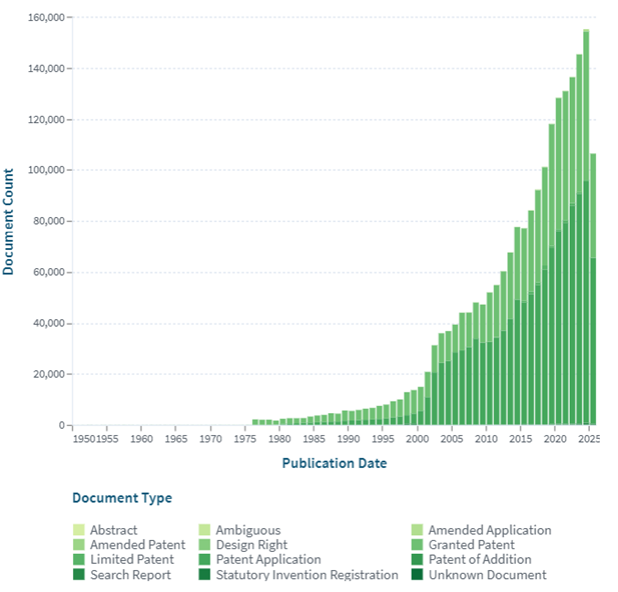
Controller-less Hand Tracking in VR Patent Documents Over Time (Source: https://www.lens.org/)
U.S. Leading the Patent Charge
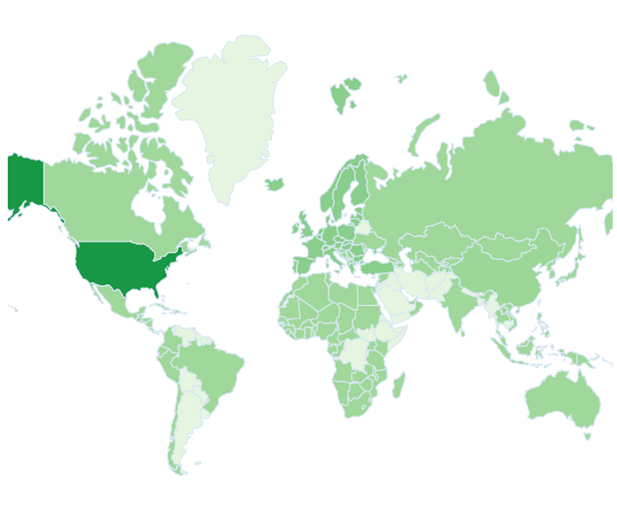
Controller-less Hand Tracking in VR Patent documents by Jurisdiction (Source: https://www.lens.org/)
Top CPC Classification Codes
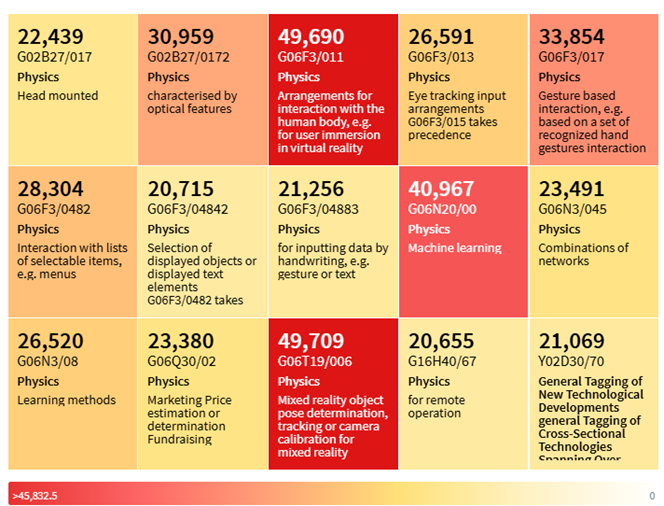
Controller-less Hand Tracking in VR Top CPC Classification Codes (Source: https://www.lens.org/)
Top IPCR Classification Codes
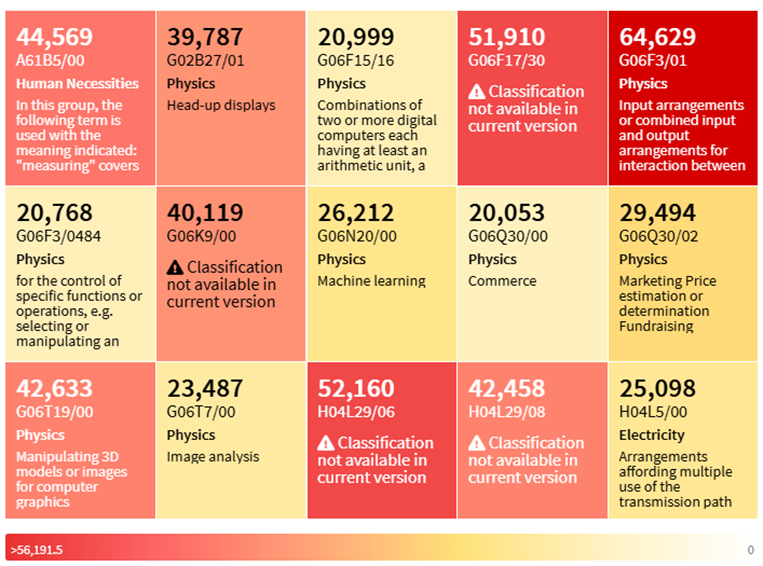
Controller-less Hand Tracking in VR Top IPCR Classification Codes (Source: https://www.lens.org/)
Market Landscape Beyond 2025
Hand tracking is becoming more competitive. Meta Quest is leading widespread adoption, improving its tracking system with each update and experimenting with EMG wristbands for extremely precise input. Controller-less input is central to Apple Vision Pro’s spatial computing experience.
While PlayStation VR still relies on controllers, Sony is likely to adopt hybrid input approaches as demand for natural interaction grows.
Companies such as HTC, Pico, and multiple startups are developing devices like smart rings and haptic gloves that add tactile feedback. These accessories aim to make interacting in virtual environments feel closer to manipulating real objects.
Market analysts expect controller-less hand tracking to become a major growth driver. The gaming market alone could reach around USD 100 billion by 2030, with strong adoption also predicted across retail, healthcare, and corporate training.
The Road Ahead
By the late 2020s, hand tracking may evolve into a multi-layered system combining:
- Vision-based gesture tracking
- EMG wristbands for micro-precision
- Haptic accessories for tactile realism
This approach could bring VR interaction closer than ever to real-world touch.
Controller-less hand tracking is not just an upgrade; it represents the future of VR engagement. Whether Meta leads in scale, Apple in refinement, or Sony in gaming, the winners will be users who interact in virtual worlds as naturally as they do in the physical one.



