Introduction:
Blockchain is a revolutionary invention that is transforming businesses and changing how we think about value exchange in the ever-evolving digital ecosystem. With the ability to secure financial transactions and promote supply chain transparency, decentralized ledger technology has enormous promise. Come us on a voyage where we’ll delve in`to the significance, the implications for intellectual property, and developing trends of blockchain technology.
Decoding Core technology and Principles
Blockchain technology is an innovative approach to digital transaction management and recordkeeping. It is predicated on the idea of a distributed database kept up to date by a computer network, known as a decentralised ledger. This implies that the ledger is not under the control of a single, central authority, making it extremely safe and impenetrable.
At the foundation of a blockchain are units of data called Blocks. A record of all transactions and a special code known as a hash are included in every block. To link blocks together and guarantee that the ledger is unchangeable, utilise the hash, which is a cryptographic fingerprint of the block.
A mathematical function known as a hash function is used to construct Hashes. This function accepts a chunk of data as input and outputs a distinct value known as a hash. No matter how long the input data is, the hash is always the same length. Because of this feature, hashes are incredibly helpful for safeguarding blockchain ledgers.
By the way of example: Let’s imagine a business that tracks the delivery of its goods using blockchain technology. A new block is added to the blockchain whenever a product is sent. The block includes details on the package, including the tracking number, origin, and destination. The new block also contains the hash from the preceding block. As a result, a blockchain, or chain of blocks, is created. The blockchain cannot be tampered as the hashes are distinct and unforgeable. The hash of a block will no longer match the hash of the previous block if someone tries to alter the data in that block and the block will be refused as a result of alerting the network to the manipulation.
Blockchain is a sophisticated technology that has a wide range of possible uses. Though it’s still in the early stages of development, it might completely change how we interact with digital information.
The core principles are:
Decentralization: Blockchain works by utilizing a peer-to-peer network to do away with middlemen and create a trustless environment in which users authenticate and record transactions together.
Cryptography: Blockchain guarantees the security and integrity of data recorded on the distributed ledger by utilizing cutting-edge cryptographic algorithms. Cryptography protects transactions against unauthorized changes or tampering by ensuring their authenticity and immutability.
Smart Contracts: Smart contracts, sometimes referred to as self-executing contracts, automate and enforce pre-established rules inside the blockchain network. These self-activating contracts improve productivity across a range of applications, simplify procedures, and increase transparency.
Unveiling the Inner Workings of Blockchain

Delving into the intricacies of blockchain technology necessitates a thorough understanding of its fundamental components:
Transaction Verification: The validation procedure is activated when a transaction is started, like sending bitcoin to another user. Network participants, or nodes, are involved in this process. Depending on the kind of blockchain (public or private), nodes can be either computers or people. These nodes carefully review the transaction to make sure it is legitimate and follows the rules of the blockchain.
Consensus Mechanisms: Consensus mechanisms are the cornerstone of blockchain operation. They are protocols created to promote agreement among all nodes in the network regarding the state of the blockchain at any given time. The proof-of-work (PoW) process is used in public blockchains like Bitcoin to reach this consensus. In order to be rewarded with Bitcoin and the ability to add a new block to the blockchain, miners compete to solve challenging mathematical riddles.
Immutable Integrity: The immutability of data on the blockchain ensures its permanence. A block’s contents are unchangeable once it is uploaded to the blockchain. Cryptographic hashing, a method that creates a distinct fingerprint for every block, protects this immutability. To change any of the data in a block, one would have to change the fingerprints of every block that came after it, which is not a computationally realistic process.
Advantages of Blockchain
- The groundwork for cryptocurrencies, blockchain technology has proven to be a game-changer with uses that extend well beyond the financial sector. Its irrevocable and decentralised nature promises to change our interactions with digital assets and reshape industries, among many other benefits. The increased security of blockchain is one of its most enticing features. Blockchain disperses data over a network of linked computers, in contrast to conventional centralised systems, making it almost impervious to hackers and unauthorised changes. This strong security structure is especially helpful in protecting private data, such bank account details and health records.
- Blockchain promotes traceability and transparency never seen before. Every transaction on the blockchain is documented in an unchangeable ledger that is available to all network users. Because of its transparency, a process can be followed and validated at every stage, which encourages responsibility and thwarts fraud. Decentralization structure of blockchain allows peer-to-peer transactions possible, which does away with the necessity for middlemen. It also lowers expenses, simplifies procedures, and gives people more authority over their assets and data.
- The adaptability of blockchain goes beyond its technological capabilities. It encourages trust and cooperation amongst network users, which makes it possible for decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) to be established. These decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) function autonomously, relying on the agreement of its members to make decisions that are democratic and to create a feeling of shared ownership.
Navigating the Intellectual Property Landscape in the Blockchain Era
With the rapid development of blockchain technology, which has fundamentally altered how people see and use digital assets, a new era of innovation and transformation has begun. Equally rapidly advancing are the intellectual property (IP) concerns related to the development and application of this technology. This article examines the subtleties of managing the intellectual property (IP) environment in the blockchain age with an emphasis on significant trends, challenges, and opportunities.
Patent Trends in Blockchain Technology
Businesses are chasing patents on blockchain technology in an attempt to protect potentially revolutionary ideas. Blockchain technology has great promise for revolutionizing several industries, such as banking, healthcare, and supply chain management.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
The increasing interest in blockchain-based financial solutions is reflected in the remarkable growth of patent applications linked to decentralized finance (DeFi). DeFi protocols provide decentralized alternatives to centralized institutions with the goal of altering established financial systems. These developments include a wide range of DeFi topics, including as lending, borrowing, and trading protocols.
Interoperability
These days, innovations that improve blockchain interoperability are the main focus of patent applications. Interoperability is the capacity of many blockchain networks to easily exchange information and communicate with one another. This is necessary in order to facilitate cross-chain transactions and encourage widespread use of blockchain technology.
Blockchain Technology Patents: Crypto assets and Beyond
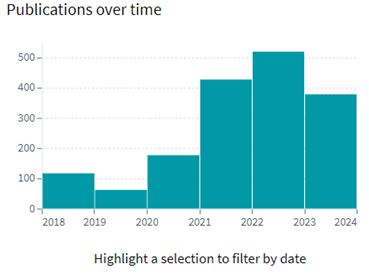
The graphs below show that for a number of years, there was an annual rise in the amount of patents filed for blockchain-related inventions, including crypto assets; however, activity has lately decreased due to various challenges in the field.
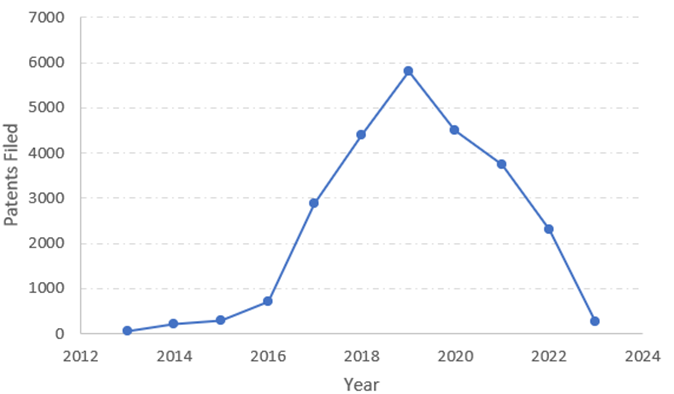
Patenting activity over the years (Source: insideglobaltech)
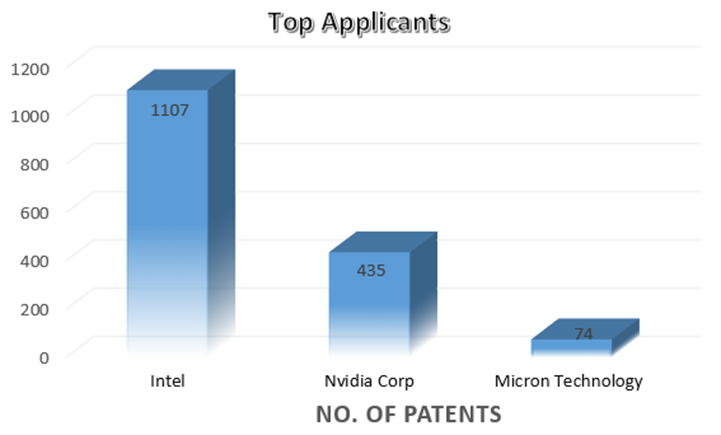
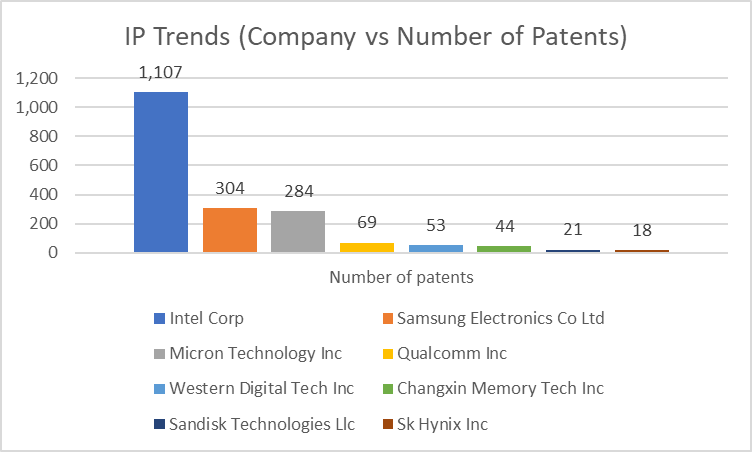
The main assignees of patent filings in the US and other nations in this field are shown in the charts below, respectively.
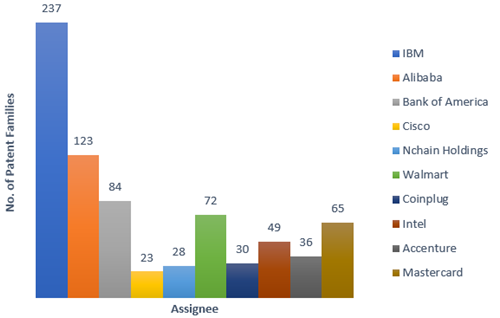
Major US Players in Blockchain patents (Source: sagaciousresearch)
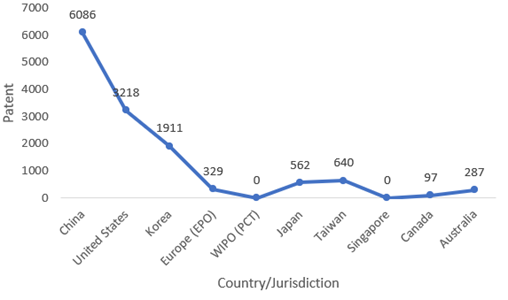
Top countries in blockchain patents in 2021 (Source: harrityllp)
Intellectual Property Challenges and Opportunities
While blockchain presents vast opportunities, navigating intellectual property challenges is crucial for sustainable innovation and growth. Key considerations include:
Open-Source Dynamics
A deliberate approach to intellectual property management is required because many blockchain initiatives are open source. When working in open-source settings, participants frequently share intellectual property rights, necessitating a delicate balance between invention protection and teamwork.
Patent Quality
To promote innovation and avoid overly broad claims, it is essential to ensure the quality of patents pertaining to blockchain technology. Patents that are too broad can stifle future innovation by limiting access to vital technology. The assessment of patent quality and its conformity to technological progress principles is largely dependent on the involvement of patent offices and industry specialists.
Current Trends and Future Trajectories
The versatility of blockchain technology is evident in its widespread adoption across various industries:
Supply Chain Management
Supply chain management is being revolutionized by blockchain technology, which improves transparency and traceability. Blockchain gives businesses the ability to follow the movement of commodities from point of origin to point of destination with an unprecedented level of precision and transparency by generating an unchangeable record of transactions. Improved traceability guarantees product legitimacy, keeps fake goods out of the market, and makes inventory management easier.
Healthcare
Blockchain is revolutionizing the healthcare sector by enhancing patient record accessibility, security, and data integrity. The tamper-proof and secure nature of blockchain guarantees the protection of sensitive patient data while facilitating easy access to vital medical information for authorized healthcare practitioners.
Integration with Emerging Technologies
Blockchain synergizes with other cutting-edge technologies to create innovative solutions that address a wide range of challenges.
Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT devices may share data with one other in a transparent and safe manner when blockchain and IoT are combined. In a variety of applications, including smart cities, industrial automation, and precision agriculture, this may help with real-time data processing, predictive maintenance, and automated decision-making.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Exploring how blockchain and AI interact might greatly improve data security and privacy. In addition to preserving the integrity and safety of sensitive data, blockchain’s decentralized and unchangeable structure may support AI’s data-driven insights by allowing AI models to function safely and independently.
Conclusion
The rapid advancement of blockchain technology necessitates careful consideration of the complexities of intellectual property (IP) management. Companies and people need to be proactive in navigating the distinct intellectual property (IP) landscape that surrounds blockchain breakthroughs in order to guarantee that their innovative concepts and works of art are suitably safeguarded. Through an awareness of the intricacies surrounding intellectual property in the context of blockchain technology, interested parties may make the most of this revolutionary tool, all the while protecting their proprietary knowledge and promoting a robust innovation community.